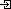Spectrum Tour offer Naranbagh Lake Kashmir, Naranbagh Lake in India, Naranbagh Lake in Srinagar Kashmir |
Jammu Kashmir Tourism » Naranbagh Lake Kashmir
Naranbagh Lake in India
Location: 30 km from Srinagar
city, Baramulla district, Jammu & Kashmir
Area: 24.3 ha
Altitude: 1587 m
Biogeographical province: 2.39.12
Wetland type: 13
Description of site: Naranbagh is a small, shallow lake on the floodplain of the river Jhelum. The lake is classified as semi-drainage type with its water supply coming mainly from the springs present within the basin. Its maximum depth is 5 m. The lake water is alkaline, with pH ranging from 7.6 - 8. The lake is characterised by ‘marl’ formation (CaCO3 precipitation) covering the macrophytic vegetation and basin sediment
Climatic conditions: The climate shows marked seasonal changes. The temperature fluctuates from -4°C in winter to 32.5°C in summer. Heavy snowfall occurs during winter
Principal vegetation: The dominant macrophytic association is Ceratophyllum-Myriophyllum which occurs throughout the deeper parts of the lake. Phragmites and Typha usually form the sheltered areas along the lake shore whereas Salvinia natans is found growing luxuriantly. Phytoplankton population shows marked seasonal changes. Chlorophyceae is dominant, followed by Bacillarophyceae and Cyanophyceae
Land tenure: State owned
Conservation measures taken: None
Conservation measures proposed: No information
Land use: The lake is used for fishing
Disturbances and threats: The lake is facing rapid eutrophication due to biotic stress
Economic and social values: The local villagers are dependent on the lake for fish, drinking water, and other domestic needs
Fauna: No information
Special floral values: None known
Related Tour Packages & information
Area: 24.3 ha
Altitude: 1587 m
Biogeographical province: 2.39.12
Wetland type: 13
Description of site: Naranbagh is a small, shallow lake on the floodplain of the river Jhelum. The lake is classified as semi-drainage type with its water supply coming mainly from the springs present within the basin. Its maximum depth is 5 m. The lake water is alkaline, with pH ranging from 7.6 - 8. The lake is characterised by ‘marl’ formation (CaCO3 precipitation) covering the macrophytic vegetation and basin sediment
Climatic conditions: The climate shows marked seasonal changes. The temperature fluctuates from -4°C in winter to 32.5°C in summer. Heavy snowfall occurs during winter
Principal vegetation: The dominant macrophytic association is Ceratophyllum-Myriophyllum which occurs throughout the deeper parts of the lake. Phragmites and Typha usually form the sheltered areas along the lake shore whereas Salvinia natans is found growing luxuriantly. Phytoplankton population shows marked seasonal changes. Chlorophyceae is dominant, followed by Bacillarophyceae and Cyanophyceae
Land tenure: State owned
Conservation measures taken: None
Conservation measures proposed: No information
Land use: The lake is used for fishing
Disturbances and threats: The lake is facing rapid eutrophication due to biotic stress
Economic and social values: The local villagers are dependent on the lake for fish, drinking water, and other domestic needs
Fauna: No information
Special floral values: None known
Related Tour Packages & information
| India Tour Packages | Travel Destinations | Europe Tour Packages | England Tour Packages | |
| America Tourism | Australia Tourism | France Tourism | Ireland Tourism | Outbound Tour Packages |
| Thailand Tourism | India Tourism | New Zealand Tourism | West Indies Tourism | Articals |