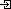Spectrum Tour offer The lake and marshes, Shallabugh Lake and Marshes, riverine marshes, Kashmir Valley, Lakes in Srinagar Kashmir, Lakes in India |
Jammu Kashmir Tourism » The lake and marshes
Shallabugh Lake and Marshes
Location: in the Kashmir Valley,
16 km northwest of Srinagar, Jammu & Kashmir
Area: 750 ha
Altitude: 1580m
Wetland type: 13,14 35
Description of site: A large area of riverine marshes and a shallow freshwater lake with associated reed-beds on the floodplain of the Jhelum river in the Kashmir valley. The are fed by the Sindh river and local run-off. The water level fluctuates considerably according to local rainfall, and large areas of the lake dry out between September and March. The depth of water varies from 0.3-2.0 m
Climatic conditions: Sub-mediterranean climate with very warm and relatively dry summers, and cold, wet winters with some precipitation in the form of snow Principal vegetation: Extensive reed-beds of Phragmites communis and Typha angustata, and a rich growth of Nymphaea candida and Nymphaea stellata in open-water areas. Lemna gibba forms mats over the surface in some waters, and plantations of willows (Salix sp.) and rice paddies grow adjacent areas
Land tenure: The wetland is state-owned (Government of Jammu & Kashmir); surrounding areas are owned by local villagers
Conservation measures taken: The entire wetland is protected as a game reserve by the Department of Wildlife Protection of Jammu & Kashmir. Reed-cutting and waterfowl hunting are permitted within the reserve under the strict control of the Department
Conservation measures proposed: There are plans to raise the bunds around the lake and to install sluice gate so that high water levels can be maintained
Land use: Waterfowl hunting in winter, harvesting of reeds in summer, and some fishing. Willows and osiers are cultivated along the periphery of the marsh, and livestock are grazed in the marshes and adjacent pastures. Surrounding areas are almost entirely agricultural
Disturbances and threats: The principal threats are siltation, eutrophication, and encroachment of agricultural land. Natural and artificial fertilisers used on adjacent agricultural land enter the lake in run-off and have greatly increased the rate of eutrophication. As the bed of the lake silts up, the marshes and floating gardens become consolidated and this encourages agricultural encroachment
Economic and social values: The wetland supports a locally important fishery and reed-harvesting industry, and provides excellent opportunities for sport hunting and scientific research
Fauna: An important staging and wintering area for migratory Anatidae, and a breeding area for a variety of waterfowl. Over 6000 ducks have been recorded at one time, the commoner Common breeding birds include Gallinula chloropus and the kingfishers Alcedo atthis, Halcyon smyrnensis, and Ceryle rudis Mammals known to occur in the reserve include Lutra lutra, Vulpes vulpes, and Canis aureus. The lake supports a rich fish fauna with species such as Cyprinus carpio
Research and facilities: Research has been conducted on the hydrology of the lake, and the Department of Wildlife Protection has carried out some waterfowl censuses
Related Tour Packages & information
Area: 750 ha
Altitude: 1580m
Wetland type: 13,14 35
Description of site: A large area of riverine marshes and a shallow freshwater lake with associated reed-beds on the floodplain of the Jhelum river in the Kashmir valley. The are fed by the Sindh river and local run-off. The water level fluctuates considerably according to local rainfall, and large areas of the lake dry out between September and March. The depth of water varies from 0.3-2.0 m
Climatic conditions: Sub-mediterranean climate with very warm and relatively dry summers, and cold, wet winters with some precipitation in the form of snow Principal vegetation: Extensive reed-beds of Phragmites communis and Typha angustata, and a rich growth of Nymphaea candida and Nymphaea stellata in open-water areas. Lemna gibba forms mats over the surface in some waters, and plantations of willows (Salix sp.) and rice paddies grow adjacent areas
Land tenure: The wetland is state-owned (Government of Jammu & Kashmir); surrounding areas are owned by local villagers
Conservation measures taken: The entire wetland is protected as a game reserve by the Department of Wildlife Protection of Jammu & Kashmir. Reed-cutting and waterfowl hunting are permitted within the reserve under the strict control of the Department
Conservation measures proposed: There are plans to raise the bunds around the lake and to install sluice gate so that high water levels can be maintained
Land use: Waterfowl hunting in winter, harvesting of reeds in summer, and some fishing. Willows and osiers are cultivated along the periphery of the marsh, and livestock are grazed in the marshes and adjacent pastures. Surrounding areas are almost entirely agricultural
Disturbances and threats: The principal threats are siltation, eutrophication, and encroachment of agricultural land. Natural and artificial fertilisers used on adjacent agricultural land enter the lake in run-off and have greatly increased the rate of eutrophication. As the bed of the lake silts up, the marshes and floating gardens become consolidated and this encourages agricultural encroachment
Economic and social values: The wetland supports a locally important fishery and reed-harvesting industry, and provides excellent opportunities for sport hunting and scientific research
Fauna: An important staging and wintering area for migratory Anatidae, and a breeding area for a variety of waterfowl. Over 6000 ducks have been recorded at one time, the commoner Common breeding birds include Gallinula chloropus and the kingfishers Alcedo atthis, Halcyon smyrnensis, and Ceryle rudis Mammals known to occur in the reserve include Lutra lutra, Vulpes vulpes, and Canis aureus. The lake supports a rich fish fauna with species such as Cyprinus carpio
Research and facilities: Research has been conducted on the hydrology of the lake, and the Department of Wildlife Protection has carried out some waterfowl censuses
Related Tour Packages & information
| India Tour Packages | Travel Destinations | Europe Tour Packages | England Tour Packages | |
| America Tourism | Australia Tourism | France Tourism | Ireland Tourism | Outbound Tour Packages |
| Thailand Tourism | India Tourism | New Zealand Tourism | West Indies Tourism | Articals |